Updated by the Progyny Clinical Team — June 2025
Pregnancy is a remarkable journey, marked by many physical and emotional changes. For some people though, it can be complicated by gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy, impacting around 1 in 12 pregnancies. Managing this condition is vital for the health of the birthing parent and the baby.
Understanding gestational diabetes
During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that make the pregnant person more resistant to insulin. Their blood sugar rises, making sure that the baby gets all the nutrients they need to grow.
For some parents though, this increased insulin resistance causes the development of gestational diabetes. This condition usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can cause serious problems if it isn’t treated.
Parents with gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of complications such as high blood pressure, premature birth, and delivering larger babies. Larger babies can have more difficulty navigating the birth canal. That can lead to birth injuries, increased risk of C-section delivery, or trouble for babies to maintain their own blood sugar after delivery.
Fortunately, through exercise, diet, and sometimes medications, gestational diabetes can be managed to support a healthy pregnancy. If medication is needed, it only means the parent’s body needs more help than their diet and exercise can give.
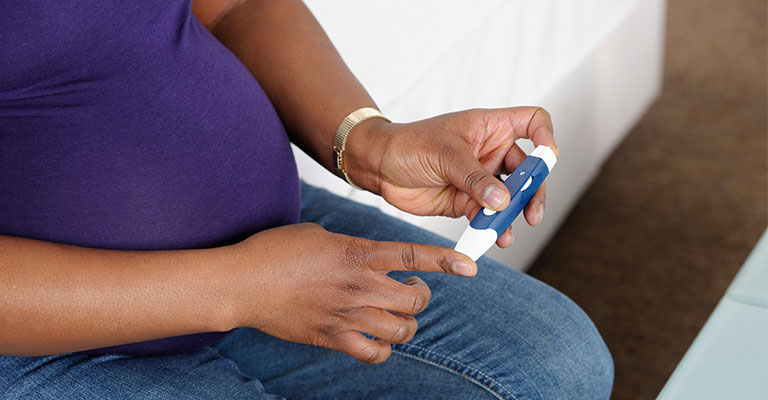
Regular prenatal screening and care
This is essential for diagnosis and management. Gestational diabetes is tested for during routine screening, typically using a glucose tolerance test.
In these tests, the parent drinks a sugary drink and then gets their blood sugar level measured. If the diagnosis is made, then at-home fingerstick tests are needed to measure the blood sugar in the morning and after meals.
While these fingerstick tests can be annoying, they are essential for treating gestational diabetes and keeping the pregnancy healthy. The tests let the healthcare provider and team understand the parent’s pregnancy and help them fine tune treatments, if needed.
The role of exercise
Exercise plays a major role in managing gestational diabetes. Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood sugar levels.
Parents should talk to their provider before starting an exercise routine. This is to make sure that it is safe and appropriate for their specific situation. Typically, a combination of aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming, or low-impact aerobics, along with strength training, can be beneficial. Even short walks after meals can help bring down blood sugar.
Maintaining a healthy diet
Diet plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Parents should focus on a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Monitoring carbohydrate intake is particularly important, as they have the most direct impact on blood sugar levels. Pregnant people are advised to spread their carbohydrate intake throughout the day to prevent blood sugar spikes.
Another recommendation is to choose foods with a low glycemic index. Eating regular, small meals can also help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Avoid simple carbohydrates, such as white grains, chips, and soda, and try to incorporate more protein, whole wheat grains, and vegetables.
Treatment and medication
In some cases, insulin or other medications may be necessary to maintain blood sugar levels at goal. For many people, needing medication can feel frustrating, but it’s often an important step to help keep both the pregnant person and their baby healthy.
Close teamwork between expecting parents and their providers is key to creating a practical and realistic care plan.
After pregnancy
After delivery, parents are at higher risk for developing gestational diabetes in a future pregnancy and non-pregnancy related diabetes later in life. It’s important to continue the healthy exercise and diet changes made while pregnant — and connect with a primary care provider for ongoing screening and care too.
Summary
Managing gestational diabetes through diet and exercise is an important part of a healthy pregnancy. By working with your provider, you can control it and reach a healthy outcome.
Progyny is here for you. If you have any questions, please contact your Progyny Care Advocate for support.
Disclaimer: The information provided by Progyny is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical guidance.