Updated by the Progyny Clinical Team — December 2025.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal condition that affects about 10% of people with ovaries during their reproductive years.
PCOS can make ovulation and menstrual periods irregular, which may impact your ability to get pregnant. It also affects your hormone and insulin levels. While PCOS has no cure, it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication — making periods more regular and improving fertility.
Top symptoms of PCOS
- Irregular periods or no periods
- Excess hair growth, especially on the face
- Acne or oily skin
- Weight gain, often around the waist
- Hair thinning or hair loss
- Darkened patches of skin or skin tags
- Difficulty getting pregnant
What your doctor may look for
Your doctor may use a combination of your medical history, physical exam, blood work, and imaging to understand what’s going on. They may look for:
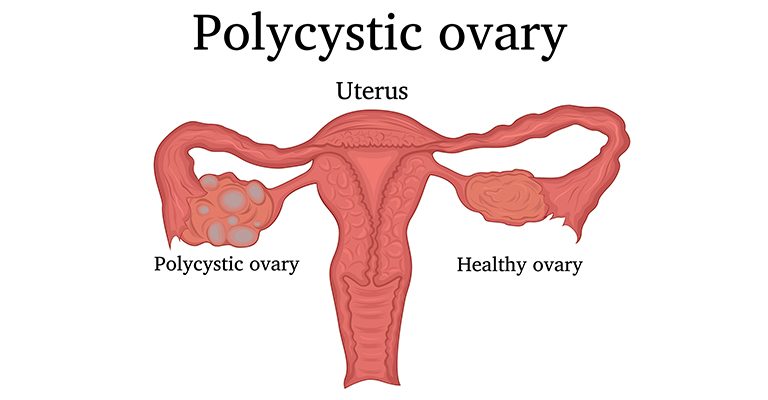
- Multiple ovarian cysts or polycystic ovaries
- Irregular or absent periods
- Elevated androgens, which are hormones typically higher in men
- High insulin levels or insulin resistance
- Signs of heart or blood vessel issues
Ways to manage PCOS
A reproductive endocrinologist (REI) or obstetrician-gynecologist (OB-GYN) can help you manage symptoms. Treatment often focuses on improving hormone balance, insulin levels, and overall health.
- Choose more whole foods, and limit sugar, sodium, and trans fats
- Stay active to support a healthy weight
- Use birth control pills to regulate hormones
- Use metformin to improve insulin sensitivity
- Treat acne with prescribed skin medications
- Reduce excess hair growth with medication for hirsutism
Fertility treatment options
If you are trying to get pregnant, a gynecologist or REI may recommend certain medications or fertility treatments to support ovulation and improve your chances of conceiving.
Common medications used to induce ovulation include:
- Oral medications, such as letrozole or clomiphene (Clomid), help stimulate the ovaries to release an egg.
- Injectable medications, such as human chorionic gonadotropin or similar injectable hormones, trigger ovulation or support the ovulation process.
Fertility treatments
- Timed intercourse: your care team tracks ovulation with ultrasounds and blood work and guides you on the best timing for intercourse.
- Intrauterine insemination: sperm is placed directly into your uterus with a thin catheter during ovulation.
- Ovulation induction: hormonal medication is given to stimulate the ovaries to ovulate, improving your chance of getting pregnant.
- In vitro fertilization: your ovaries are stimulated with medication, your eggs are retrieved and fertilized in a lab, and an embryo is transferred into your uterus.
Pregnancy is possible
PCOS is a leading cause of infertility, but many people with PCOS do get pregnant. If you are thinking about building your family, talk with your OB-GYN or an REI to explore your options and create a plan that works for you.
If you have questions, Progyny is here for you. Please contact your Progyny Care Advocate for support.
Disclaimer: The information provided by Progyny is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for medical guidance.